Which Are The Main Reasons For Overpronation Of The Feet
Overview
The way your foot rolls when it hits the ground is known as pronation, and if you're a runner, it's essential to know what type of pronator you are. There are three types, normal pronation, overpronation, and underpronation (supination). Figuring out your running pattern will help you buy the right running shoe. Not only will this make running more comfortable, but it can also help prevent future injury.
Causes
There are many possible causes for overpronation, but researchers have not yet determined one underlying cause. Hintermann states, Compensatory overpronation may occur for anatomical reasons, such as a tibia vara of 10 degrees or more, forefoot varus, leg length discrepancy, ligamentous laxity, or because of muscular weakness or tightness in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Pronation can be influenced by sources outside of the body as well. Shoes have been shown to significantly influence pronation. Hintermann states that the same person can have different amounts of pronation just by using different running shoes. It is easily possible that the maximal ankle joint eversion movement is 31 degrees for one and 12 degrees for another running shoe.
Symptoms
Common conditions seen with overpronation include heel pain or plantar fasciitis. Achilles tendonopathy. Hallus Valgus and/or bunions. Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Iliotibial band pain syndrome. Low back pain. Shin splints. Stress fractures in the foot or lower leg.
Diagnosis
The best way to discover whether you have a normal gait, or if you overpronate, is to visit a specialty run shop, an exercise physiologist, a podiatrist or a physical therapist who specializes in working with athletes. A professional can analyze your gait, by watching you either walk or run, preferably on a treadmill. Some facilities can videotape your gait, then analyze the movement of your feet in slow-motion. Another (and less costly) way is to look at the bottom of an older pair of run shoes. Check the wear pattern. A person with a normal gait will generally see wear evenly across the heel and front of the shoe. A person who overpronates will likely see more wear on the OUTside of the heel and more wear on the INside of the forefoot (at the ball). A person who supinates will see wear all along the outer edges of the shoe. You can also learn about your gait by looking at your arches. Look at the shape your wet feet leave on a piece of paper or a flat walking surface.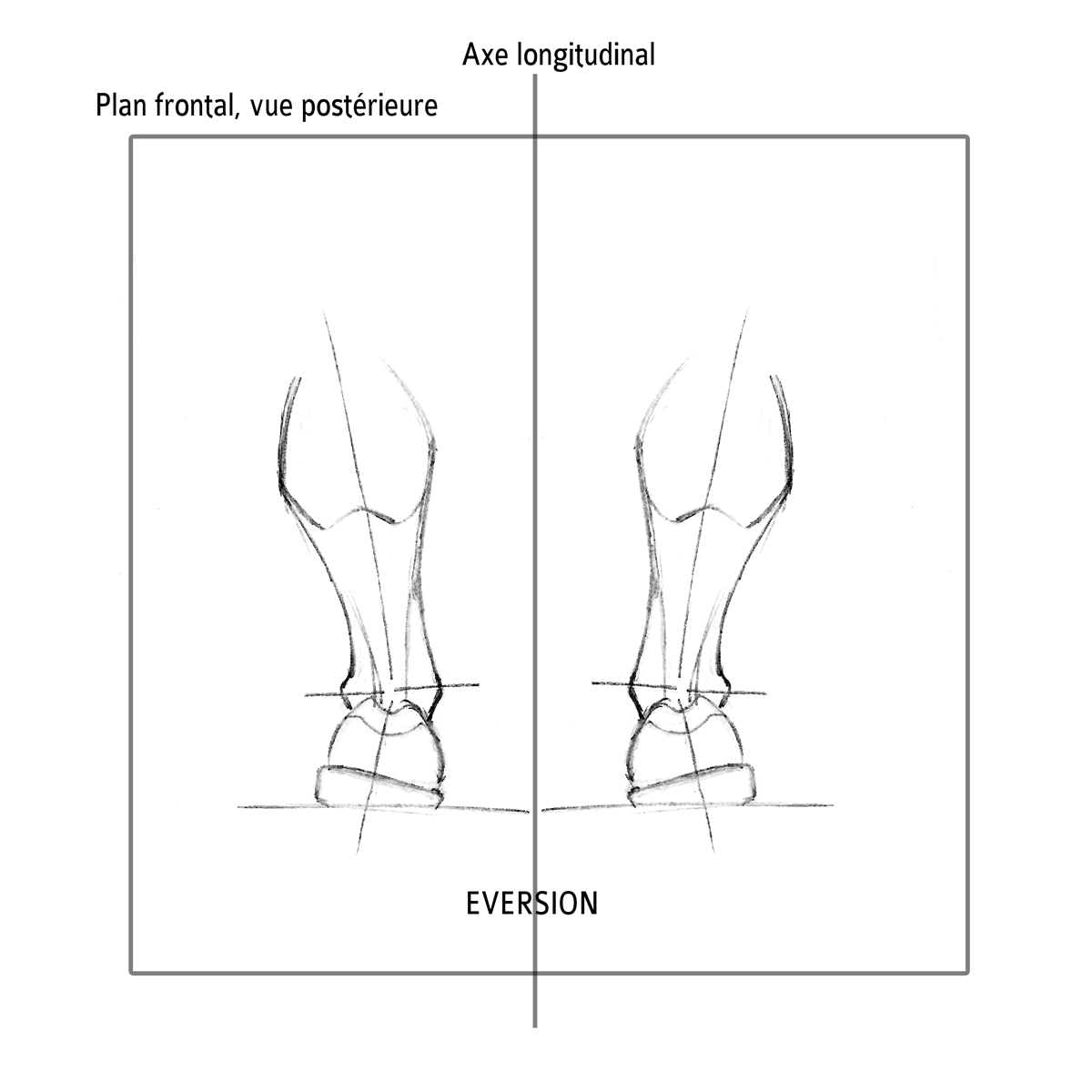
Non Surgical Treatment
Podiatrists are trained to effectively detect and management over-pronation. You can get a referral to a podiatrist from your GP if you are presenting with the pain typical of over-pronation, or you can seek private podiatric care in anyone of several registered and accredited practices across the country. Your podiatrist will examine your foot and its shape to determine whether or not over-pronation is the cause of your pain. If your podiatrist determines that it is a problem with arch support that is giving you trouble, then they can effectively remedy that lack of support with orthotics.
Prevention
Exercises to strengthen and stretch supporting muscles will help to keep the bones in proper alignment. Duck stance: Stand with your heels together and feet turned out. Tighten the buttock muscles, slightly tilt your pelvis forwards and try to rotate your legs outwards. You should feel your arches rising while you do this exercise. Calf stretch: Stand facing a wall and place hands on it for support. Lean forwards until stretch is felt in the calves. Hold for 30 seconds. Bend at knees and hold for a further 30 seconds. Repeat 5 times. Golf ball: While drawing your toes upwards towards your shins, roll a golf ball under the foot between 30 and 60 seconds. If you find a painful point, keep rolling the ball on that spot for 10 seconds. Big toe push:
Stand with your ankles in a neutral position (without rolling the foot inwards). Push down with your big toe but do not let the ankle roll inwards or the arch collapse. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Build up to longer times and fewer repetitions. Ankle strengthener: Place a ball between your foot and a wall. Sitting down and keeping your toes pointed upwards, press the outside of the foot against the ball, as though pushing it into the wall. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times. Arch strengthener: Stand on one foot on the floor. The movements needed to remain balanced will strengthen the arch. When you are able to balance for 30 seconds, start doing this exercise using a wobble board.
The way your foot rolls when it hits the ground is known as pronation, and if you're a runner, it's essential to know what type of pronator you are. There are three types, normal pronation, overpronation, and underpronation (supination). Figuring out your running pattern will help you buy the right running shoe. Not only will this make running more comfortable, but it can also help prevent future injury.

Causes
There are many possible causes for overpronation, but researchers have not yet determined one underlying cause. Hintermann states, Compensatory overpronation may occur for anatomical reasons, such as a tibia vara of 10 degrees or more, forefoot varus, leg length discrepancy, ligamentous laxity, or because of muscular weakness or tightness in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Pronation can be influenced by sources outside of the body as well. Shoes have been shown to significantly influence pronation. Hintermann states that the same person can have different amounts of pronation just by using different running shoes. It is easily possible that the maximal ankle joint eversion movement is 31 degrees for one and 12 degrees for another running shoe.
Symptoms
Common conditions seen with overpronation include heel pain or plantar fasciitis. Achilles tendonopathy. Hallus Valgus and/or bunions. Patellofemoral pain syndrome. Iliotibial band pain syndrome. Low back pain. Shin splints. Stress fractures in the foot or lower leg.
Diagnosis
The best way to discover whether you have a normal gait, or if you overpronate, is to visit a specialty run shop, an exercise physiologist, a podiatrist or a physical therapist who specializes in working with athletes. A professional can analyze your gait, by watching you either walk or run, preferably on a treadmill. Some facilities can videotape your gait, then analyze the movement of your feet in slow-motion. Another (and less costly) way is to look at the bottom of an older pair of run shoes. Check the wear pattern. A person with a normal gait will generally see wear evenly across the heel and front of the shoe. A person who overpronates will likely see more wear on the OUTside of the heel and more wear on the INside of the forefoot (at the ball). A person who supinates will see wear all along the outer edges of the shoe. You can also learn about your gait by looking at your arches. Look at the shape your wet feet leave on a piece of paper or a flat walking surface.

Non Surgical Treatment
Podiatrists are trained to effectively detect and management over-pronation. You can get a referral to a podiatrist from your GP if you are presenting with the pain typical of over-pronation, or you can seek private podiatric care in anyone of several registered and accredited practices across the country. Your podiatrist will examine your foot and its shape to determine whether or not over-pronation is the cause of your pain. If your podiatrist determines that it is a problem with arch support that is giving you trouble, then they can effectively remedy that lack of support with orthotics.
Prevention
Exercises to strengthen and stretch supporting muscles will help to keep the bones in proper alignment. Duck stance: Stand with your heels together and feet turned out. Tighten the buttock muscles, slightly tilt your pelvis forwards and try to rotate your legs outwards. You should feel your arches rising while you do this exercise. Calf stretch: Stand facing a wall and place hands on it for support. Lean forwards until stretch is felt in the calves. Hold for 30 seconds. Bend at knees and hold for a further 30 seconds. Repeat 5 times. Golf ball: While drawing your toes upwards towards your shins, roll a golf ball under the foot between 30 and 60 seconds. If you find a painful point, keep rolling the ball on that spot for 10 seconds. Big toe push:
Stand with your ankles in a neutral position (without rolling the foot inwards). Push down with your big toe but do not let the ankle roll inwards or the arch collapse. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Build up to longer times and fewer repetitions. Ankle strengthener: Place a ball between your foot and a wall. Sitting down and keeping your toes pointed upwards, press the outside of the foot against the ball, as though pushing it into the wall. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times. Arch strengthener: Stand on one foot on the floor. The movements needed to remain balanced will strengthen the arch. When you are able to balance for 30 seconds, start doing this exercise using a wobble board.